Tech
UXUI
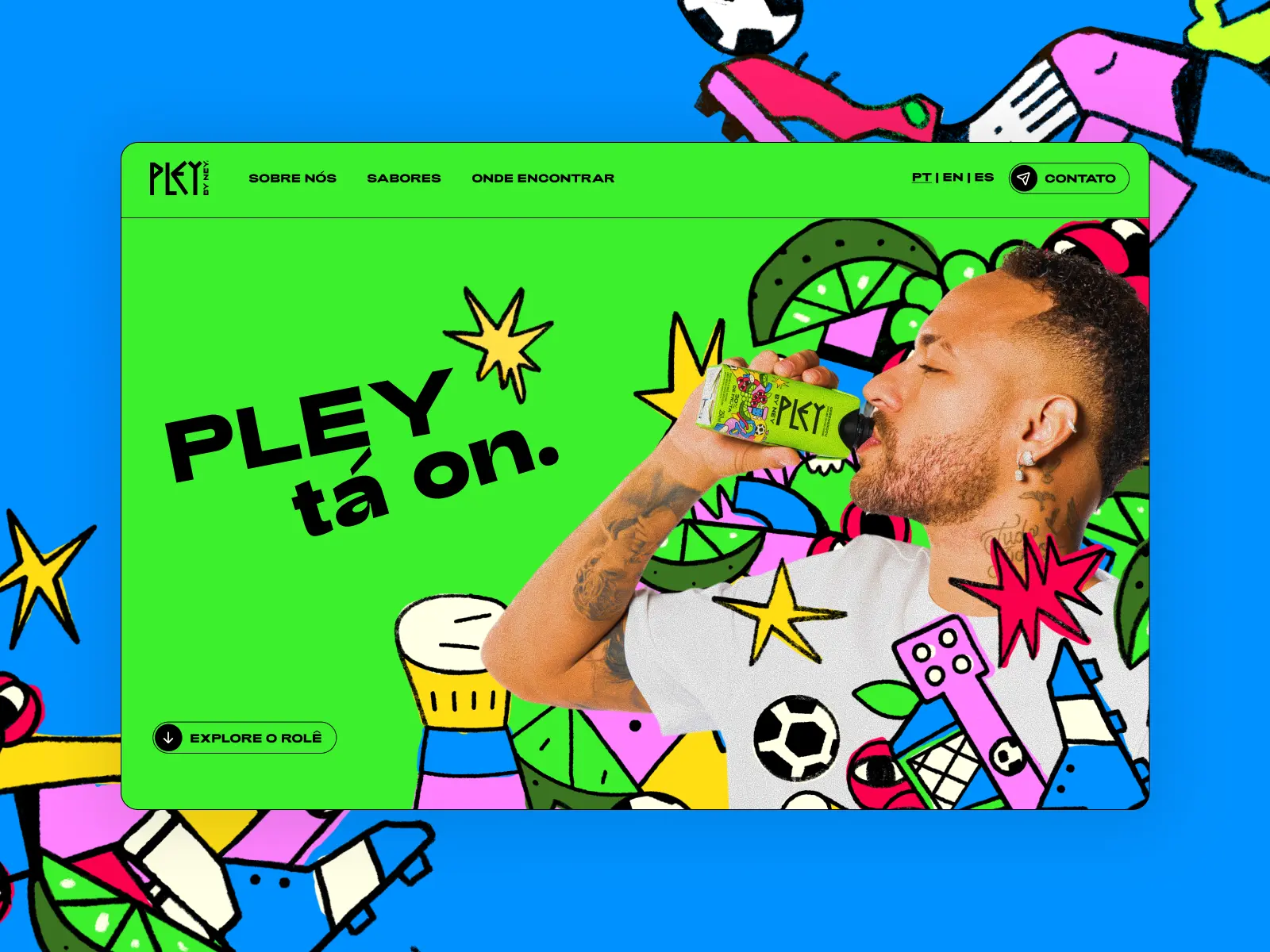
Websites
Websites

THE digital accessibility refers to the ability of a person with a disability to access and use online content, such as websites, applications and social networks. It is important to highlight that digital accessibility is not a matter of convenience, but rather of right. Ensuring digital accessibility is essential for the digital inclusion of people with disabilities, who often face barriers to accessing information, services and opportunities available online.
In Brazil, according to data from the Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics (IBGE), approximately 251,000 people (approximately 45 million) have some type of disability. Of this total, more than 6.5 million have visual impairment, more than 2.7 million have hearing impairment, more than 13 million have motor impairment and approximately 1.4 million have intellectual impairment.
The lack of digital accessibility can prevent these people from fully participating in the social, cultural and economic life of the country. Without access to websites and applications that offer information and services, such as health, employment and education, people with disabilities may be excluded from these opportunities. In addition, the lack of digital accessibility can affect the autonomy and independence of these people, limiting their leisure, communication and relationship options.
Ensuring digital accessibility is essential to promoting social inclusion and equal opportunities for all people, regardless of their disabilities. Companies, governments and technology developers have an important role to play in ensuring that their products and services are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
Digital accessibility must take into account the various disabilities that can affect a user’s experience with online content. Some of the most common types of disabilities are:
By taking these types of disabilities into account, it is possible to make digital content accessible to a wide range of users, including those with multiple or complex disabilities.
Businesses can play an important role in promoting digital accessibility for people with disabilities in their communication channels. Some ways businesses can improve accessibility include:
By promoting digital accessibility across their communication channels, companies can help ensure that people with disabilities have equal access to the content and services they offer, as well as contributing to a more inclusive and fair society.
Accessibility testing in real scenarios with people with disabilities is essential to ensure that the solutions proposed in projects are effectively accessible and usable by people with different types of disabilities.
While it is possible to follow accessibility best practices and guidelines, the only way to ensure that a website or application is truly accessible is to test it in real-world scenarios with people with disabilities. This is because every person with a disability has different needs and preferences, and only by testing digital content with these people can you ensure that it is truly accessible.
Real-world accessibility testing can include activities such as usability testing, accessibility testing, and assessments of compliance with accessibility guidelines. It allows companies to identify accessibility issues and find solutions to them, ensuring that digital content is accessible to everyone.
Additionally, conducting accessibility testing in real-world scenarios with people with disabilities can be an important way to involve and include them in the website or app development process. This can help companies better understand the needs and preferences of people with disabilities, as well as promote inclusion and equal access to content.
Therefore, accessibility testing in real scenarios with people with disabilities is a fundamental step to validate the solutions proposed in digital accessibility projects and ensure that the content is truly accessible for everyone.
Digital accessibility is a matter of citizenship, as equal access to information and services is a fundamental right of all people, regardless of their physical, sensory or cognitive condition. Digital exclusion can limit access to information, services and opportunities, hindering people's participation in society.
Digital inclusion is therefore a matter of social justice and equity, as all people should have the same opportunities to access digital information, services and resources. This includes access to websites, mobile applications, e-commerce systems, social media platforms and other digital resources.
When companies invest in digital accessibility, they are helping to ensure that all people have equal access to the information and services they need to live their daily lives. This includes people with disabilities, seniors, people with low digital literacy, and others who may have difficulty accessing digital information.
By promoting digital accessibility, companies are not only fulfilling a legal or ethical obligation, but they are also helping to build a more inclusive and equal society, where all people can fully participate and have access to the same rights and opportunities.
In short, digital accessibility is a citizenship issue, ensuring that all people have equal access to digital information and services. When companies promote digital accessibility, they are helping to build a more inclusive and equal society, promoting social justice and equity.
In addition to being a matter of citizenship and social responsibility, promoting digital accessibility also brings significant benefits to companies. Below are some of the main benefits that companies can obtain by promoting digital accessibility:
By investing in digital accessibility, companies can not only fulfill their social responsibility, but also improve their competitive position and stand out in the market.
The government plays a fundamental role in promoting digital accessibility, as it is responsible for ensuring that all citizens, regardless of their limitations, have equal access to services and information available online. In this sense, there are specific laws and regulations that seek to guarantee digital accessibility within the public sector.
In Brazil, for example, the Brazilian Law for the Inclusion of Persons with Disabilities (LBI), enacted in 2015, establishes mandatory accessibility in information and communication technology services and products. In addition, in 2018, Decree 9,508 was published, which provides for accessibility to websites and internet applications within the scope of the federal public administration.
These standards establish that all services and information provided by the government must be accessible to people with disabilities, including those with visual, hearing, physical and cognitive impairments. This means that websites and applications developed by the government must follow accessibility standards and offer features such as image descriptions, video captions, voice capabilities, among others.
It is important to emphasize that the government can also encourage the adoption of digital accessibility practices in the private sector, through policies and initiatives aimed at digital inclusion. In this way, it is possible to ensure that digital accessibility is a reality for all citizens, contributing to a more inclusive and egalitarian society.
Digital accessibility is an ever-evolving field, and as technology rapidly evolves, new solutions and capabilities are being developed to promote digital inclusion. The adoption of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and virtual reality has the potential to significantly transform the way people with disabilities interact with technology.
Artificial intelligence can be used to improve the browsing experience on websites and apps, allowing interfaces to adapt to the individual needs of each user. For example, speech recognition technology can be used to allow people with physical or visual disabilities to access content without having to use a mouse or keyboard.
Virtual reality can offer new possibilities for accessibility, allowing people with visual impairments to “see” 3D images, or people with physical disabilities to interact with virtual environments without having to physically move around.
Additionally, technology can also help improve accessibility in other areas, such as education and the workplace. For example, online learning platforms can use machine translation technology to allow people with hearing impairments to follow classes in real time.
The future prospects for digital accessibility are promising and the development of new technologies has the potential to transform the way people with disabilities interact with technology, improving their experience and promoting digital inclusion.
Digital accessibility is a key issue in ensuring inclusion and equal opportunities for people with disabilities. Lack of accessibility on websites, apps and other online platforms can prevent people with disabilities from accessing information and services, harming their quality of life and limiting their potential to participate in society.
Companies have an important role to play in promoting digital accessibility by ensuring that their communication channels are accessible to all users, regardless of their abilities and needs. An ESG approach can be a valuable strategy to promote digital accessibility and contribute to a more inclusive world.
Furthermore, it is important to emphasize the importance of accessibility testing in real scenarios with people with disabilities, in order to ensure that the solutions proposed in projects are effective and truly promote digital inclusion.
Finally, it is important to highlight that digital accessibility is a matter of citizenship and should be a concern for everyone, including companies, governments and individuals. Promoting digital accessibility not only benefits people with disabilities, but also contributes to a more just and inclusive world.

Tech
UXUI
Websites
Websites

Apps
Websites
